



Next: The Vertex Algorithm
Up: Centrality estimates using the
Previous: Centrality
Contents
ADC to Multiplicity
The first thing to be aware of is how the translation from 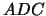 counts into
counts into 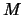 is performed5. The ADCs for the tiles are dual range ADC, so a
preliminary correction of the
is performed5. The ADCs for the tiles are dual range ADC, so a
preliminary correction of the 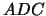 s must be done:
s must be done:
where 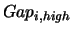 is the lower limit of the upper part of the ADC,
and
is the lower limit of the upper part of the ADC,
and 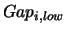 is the upper limit of the lower part of the ADC.
is the upper limit of the lower part of the ADC.
Next, we exclude all 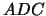 s that are are lower than a certain
threshold
s that are are lower than a certain
threshold 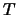 :
:
where 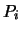 is the ADC's pedestal,
is the ADC's pedestal, 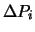 the pedestal width,
and
the pedestal width,
and 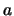 some constant factor.
some constant factor. 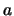 is usually set to 2.
is usually set to 2.
The next step, is to subtract the pedestal from the  values, to
give us the calibrated
values, to
give us the calibrated 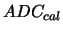 :
:
As described elsewhere [2], one must make a geometrical
correction for the spread in path length through a given tile, when
determining the individual tile multiplicity. This correction factor
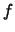 is highly vertex dependent, and is given by:
is highly vertex dependent, and is given by:
where 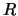 is the tile's radial distance from the beam axis,
is the tile's radial distance from the beam axis,
 the
the 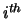 tile's position along the beam axis, and
tile's position along the beam axis, and 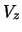 the
primary vertex position along the beam axis.
the
primary vertex position along the beam axis.
![\begin{SCfigure}
% latex2html id marker 182
[10][htbp]
%%\begin{center}
\leave...
...on factor for relative position of
tile to vertex} %%\end{center}\end{SCfigure}](AnNote22_img54.gif)
Finally, we end up with something that is more or less proportional to
the multiplicity in a given tile, by dividing by the mean deposited
energy per particle 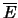 in a tile:
in a tile:
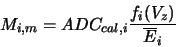 |
(4) |
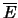 is determined from cosmic ray data [1].
is determined from cosmic ray data [1].




Next: The Vertex Algorithm
Up: Centrality estimates using the
Previous: Centrality
Contents
Christian Holm Christensen
2001-02-13
![]() counts into
counts into ![]() is performed5. The ADCs for the tiles are dual range ADC, so a
preliminary correction of the
is performed5. The ADCs for the tiles are dual range ADC, so a
preliminary correction of the ![]() s must be done:
s must be done:
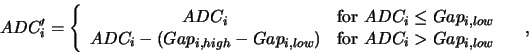
![]() s that are are lower than a certain
threshold
s that are are lower than a certain
threshold ![]() :
:
![]() values, to
give us the calibrated
values, to
give us the calibrated ![]() :
:
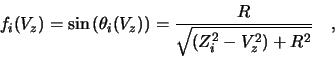
![]() in a tile:
in a tile: